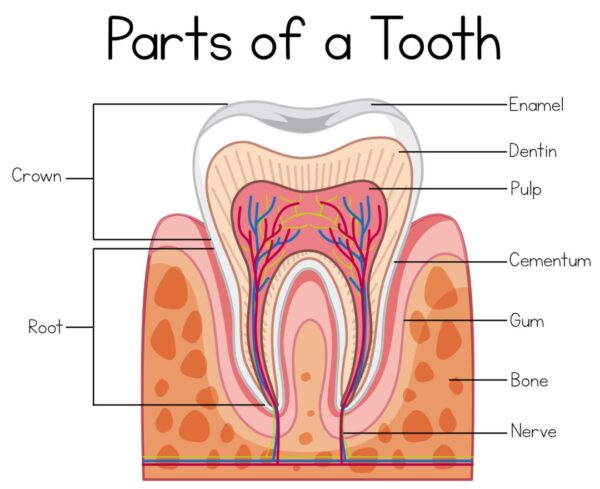
What is Dentin?
Tooth dentin is an essential component of the tooth structure, playing a crucial role in maintaining its strength and integrity. Dentin is a hard, calcified tissue that lies beneath the outer enamel layer and surrounds the inner pulp chamber of the tooth.
Composed mainly of mineralized collagen fibers, dentin provides support to the enamel and protects the delicate pulp tissue from external stimuli. It is responsible for giving teeth their characteristic color, which can vary from yellowish to grayish depending on factors such as age and genetics.
Dentin contains tiny channels called dentinal tubules that extend from the outer surface towards the pulp chamber. These tubules house nerve endings that transmit sensations such as temperature or pressure to the dental pulp, allowing us to perceive different stimuli.
Tooth Dentin and Your Dental Health
From diagnosing dental conditions to determining appropriate treatment options, understanding the condition of your tooth dentin helps us provide effective dental care for you and can help you maintain optimal oral hygiene.
What is the purpose of tooth dentin?
Dentin, a vital component of teeth, plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall structure and function of your oral cavity. Located beneath the outer layer of enamel and surrounding the inner pulp chamber, dentin serves as a protective layer for the delicate nerves and blood vessels within your tooth.
One of the primary functions of dentin is to provide support and strength to the tooth structure. It acts as a cushioning material that absorbs external forces during chewing or biting, preventing damage to the underlying pulp.
Dentin & Tooth Sensitivity
Dentin also contributes to tooth sensitivity. It contains tiny tubules that connect with nerve endings in the pulp, allowing sensations such as temperature or pressure to be transmitted to our brain. This sensitivity helps us discern between hot and cold foods or identify potential dental issues




